Bridging the Gap: Medication Solutions for Social Anxiety Disorder
This article includes two recommendations for online psychiatry services, where qualified professionals can evaluate individuals with social anxiety, provide a diagnosis, and prescribe medication, if suitable. By using our links, you may receive a significant discount on these services, and we will receive a commission.
Living with social anxiety can be an overwhelming and distressing experience. The fear of judgment, embarrassment, or scrutiny can make even the simplest social interactions feel daunting.
If you’re one of the millions of individuals grappling with social anxiety disorder, it’s important to know that you’re not alone, and there are effective treatment options available to help you overcome this challenge.

While therapy and lifestyle modifications are valuable components of social anxiety treatment, medication can also play a significant role in managing the symptoms and improving your overall well-being.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of medication for social anxiety disorder, exploring its benefits, limitations, and the different types of medications commonly prescribed.
By understanding the options available and working closely with healthcare professionals, you can make informed decisions about your treatment journey and find the relief and empowerment you deserve.
Throughout this article, we will address various aspects of medication for social anxiety, including their mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and considerations when combining medication with therapy or other treatments.

It’s important to note that medication is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and what works for one person may not work for another.
However, this resource aims to provide you with a solid foundation of knowledge, allowing you to have informed discussions with your healthcare provider and explore the best course of action for your unique situation.
Remember, seeking professional guidance is crucial when considering medication for social anxiety. A healthcare provider can evaluate your symptoms, discuss your treatment goals, and help determine the most appropriate medication and dosage for you.
They will closely monitor your progress and make adjustments as needed, ensuring your well-being throughout the treatment process.
By educating yourself about medication for social anxiety, you’re taking an important step towards taking control of your mental health.
Are you ready? Then let’s get started!

A. Overview of Medication as a Treatment Option for Social Anxiety
Medication can be a valuable tool in the treatment of social anxiety.
When used in conjunction with therapy and other supportive strategies, it can help alleviate the distressing symptoms associated with social anxiety disorder and improve overall quality of life.
Emphasizing its critical significance, it cannot be stressed enough that medication should always be prescribed and closely monitored by a qualified healthcare professional. This crucial point will be reiterated consistently throughout this article to underscore its utmost importance.
How Medication Can Help
Medication for social anxiety aims to reduce anxiety symptoms, improve emotional well-being, and enhance the individual’s ability to engage in social situations more comfortably.
It can target both the psychological and physiological aspects of anxiety, providing relief from symptoms such as excessive worry, panic attacks, rapid heartbeat, sweating, and trembling.
More specifically, medication for social anxiety can help:
Reduce Excessive Worry: Social anxiety often involves persistent and intrusive worry about negative evaluation or embarrassment in social situations. Medication can help alleviate excessive worry, allowing individuals to approach social interactions with greater ease and less preoccupation with potential negative outcomes.
Alleviate Panic Attacks: Panic attacks, characterized by sudden and intense surges of fear or discomfort, can be a distressing symptom of social anxiety. Medication can help reduce the frequency and severity of panic attacks, enabling individuals to feel more secure and in control during challenging social encounters.
Manage Physiological Symptoms: Social anxiety is often accompanied by physiological symptoms such as a rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, and shortness of breath. Medication can help regulate the body’s stress response, reducing these physiological manifestations of anxiety and promoting a greater sense of calmness in social situations.

Quick Overview of Different Types of Medication for Social Anxiety
There are several classes of medication commonly used in the treatment of social anxiety disorder. Here’s a brief overview of these medications, and later in the article, we will provide a more in-depth exploration of each one:
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs):
SSRIs are a type of antidepressant that can help regulate serotonin levels in the brain, which is associated with mood regulation.
They are considered a first-line treatment for social anxiety and may include medications such as fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), and escitalopram (Lexapro).
By the way, don’t let the term “antidepressant” confuse you. While SSRIs are often classified as antidepressants, it’s important to note that these medications have consistently demonstrated their efficacy in not only reducing symptoms of depression but also addressing anxiety-related issues.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs):
SNRIs are another class of antidepressants that increase the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain.
They may be prescribed when SSRIs are ineffective or not well-tolerated.
Benzodiazepines:
Benzodiazepines are a class of sedative medications that work by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which has a calming effect on the brain.
They are usually prescribed for short-term use due to their potential for dependence and side effects.

Beta-Blockers:
Beta-blockers are primarily used to manage physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat, trembling, and sweating.
They work by blocking the effects of adrenaline, reducing the body’s physiological response to anxiety-inducing situations.
Other Medications:
In some cases, atypical antidepressants or monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) may be prescribed if other options have not provided sufficient relief.

B. Benefits and Limitations of Using Medication for Social Anxiety
When it comes to treating social anxiety, medication can offer several benefits. However, it’s essential to be aware of both the advantages and limitations associated with its use.
Here, we’ll explore the positive and negative aspects of medication in managing social anxiety, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of its potential impact.
Benefits of Medication
Symptom Relief
Medication can effectively alleviate the symptoms of social anxiety, including excessive fear, worry, and physical manifestations such as rapid heartbeat and sweating.
It can help individuals feel more at ease in social situations, allowing them to participate more fully in daily activities.
Improved Quality of Life
By reducing anxiety symptoms, medication can enhance overall well-being and quality of life.
It can promote better emotional stability, reduce the impact of social anxiety on relationships and work performance, and increase overall satisfaction with life.
Enhanced Therapy Outcomes
Medication can complement therapy by reducing the intensity of anxiety symptoms, making it easier for individuals to engage in therapeutic techniques and strategies.
This synergy between medication and therapy can facilitate more effective progress in managing social anxiety.

Limitations and Considerations
Individual Variability
The effectiveness of medication varies from person to person. What works well for one individual may not have the same impact on another.
It may take time to find the right medication and dosage that best suits an individual’s specific needs.
Potential Side Effects
Medication use can be associated with side effects, ranging from mild to more severe.
Common side effects of medication for social anxiety may include symptoms such as nausea, drowsiness, dizziness, or sexual dysfunction. We will delve into a more detailed discussion of these potential side effects shortly.
It’s crucial to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare professional and report any concerning symptoms promptly.
Dependency and Withdrawal
Certain medications, such as benzodiazepines, can be habit-forming if used for an extended period. Abrupt discontinuation of these medications can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
It’s important to follow healthcare provider instructions for dosage adjustments and discontinuation.

Need for Professional Guidance
Medication for social anxiety should always be prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare professional.
They can assess the individual’s needs, determine the appropriate medication and dosage, and provide ongoing monitoring to ensure its effectiveness and safety.
Addressing Underlying Causes
While medication can alleviate symptoms, it does not address the root causes of social anxiety.
It is often used in conjunction with therapy and other supportive strategies to provide a comprehensive approach to treatment.

Personalized Treatment Approach
Again, it’s essential to recognize that social anxiety treatment is highly individualized. What works for one person may not work for another.
The decision to use medication should be made in collaboration with a healthcare professional who can assess the specific needs, goals, and considerations of the individual.
Regular Evaluation and Adjustments
Medication effectiveness should be regularly evaluated, and adjustments may be necessary to optimize the treatment plan.
Open and ongoing communication with a healthcare provider is crucial to ensure that the chosen medication continues to meet the individual’s needs.

C. Different Types of Medication Used for Social Anxiety
As previously mentioned, there are several types of medication commonly prescribed to treat social anxiety.
In the following sections, we will delve into each type, providing a more comprehensive understanding of their usage in the treatment of social anxiety.

Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are considered a first-line treatment for social anxiety due to their proven effectiveness and tolerability, as supported by scientific research.
In a recent systematic review and meta-analysis of multiple studies, SSRIs demonstrated significant improvements in response rates and reduction of social anxiety symptoms compared to placebo (Mitsui et al., 2022).
The findings from the meta-analysis showed that individuals who received treatment with SSRIs had a significantly higher rate of improvement (62% higher) compared to those who received a placebo.
On average, the groups taking SSRIs experienced a reduction of 9.65 points on the Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale, which measures the severity of social anxiety symptoms. These results provide strong evidence that SSRIs can effectively alleviate the symptoms of social anxiety.
SSRIs function by increasing the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation, in the brain. By restoring the balance of serotonin, SSRIs help reduce excessive fear, worry, and avoidance behaviors commonly associated with social anxiety.
It’s important to note that SSRIs are typically taken on a daily basis and may require several weeks to reach their full effect. Despite the time delay, their proven efficacy and tolerability make them a recommended initial choice for long-term treatment of social anxiety.
By targeting serotonin levels in the brain, SSRIs offer a valuable tool in managing social anxiety and helping individuals regain control over their lives.
However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on individual circumstances and to monitor potential side effects or interactions with other medications.
For a more in-depth understanding of the treatment of social anxiety with SSRIs, please click here to access our detailed article on the mechanisms of action, symptom reduction, scientific evidence, duration of treatment and important considerations regarding the use of SSRIs.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs are a class of medications that may be considered as an alternative to SSRIs when they are ineffective or not well-tolerated in the treatment of social anxiety disorder.
These medications work by increasing the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain, providing a dual-action mechanism compared to SSRIs.
By modulating these neurotransmitters, SNRIs help regulate mood, anxiety, and the stress response, which can be beneficial for individuals with social anxiety.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of pharmacotherapy for social anxiety disorder found that SNRIs significantly improved response rates and reduced social anxiety symptoms compared to placebo (Mitsui et al., 2022).
The meta-analysis included 6 studies on SNRIs, and the findings revealed that individuals treated with SNRIs had a 57% higher response rate and, on average, an 11.72-point reduction in Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale scores compared to those who received a placebo.

These findings provide support for considering SNRIs as an additional pharmacotherapeutic option for social anxiety, especially when there is a need for dual-action treatment or when SSRIs are not sufficient in addressing the symptoms of social anxiety
Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional is essential to assess the suitability and safety of SNRIs for managing social anxiety. A comprehensive evaluation and expert advice will help determine the appropriate and effective use of SNRIs, tailored to individual needs and circumstances.
For a more in-depth understanding of SNRI treatment for social anxiety, click here to access our detailed article on mechanisms of action, symptom reduction, scientific evidence, treatment duration and important considerations when using SNRIs.

Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are sedative medications commonly used for the short-term management of anxiety symptoms.
They act as anxiolytic agents by affecting the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) system, which helps to reduce anxiety.
Rapid relief from anxiety symptoms can be achieved with benzodiazepines, making them particularly useful in situations where immediate symptom control is necessary, such as before a specific social event or during a short-term crisis (Williams et al. 2017).

However, it is important to note that benzodiazepines carry certain risks and limitations.
They have a high potential for dependence and abuse, which is why they are typically prescribed for short-term use (Licata & Rowlett, 2008).
Prolonged or excessive use of benzodiazepines can lead to tolerance, where higher doses are needed to achieve the same effect, and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation.
Therefore, long-term use of benzodiazepines for social anxiety is generally not recommended.
Due to the potential for dependence and withdrawal issues, it is essential to carefully weigh the benefits and risks of benzodiazepine use for social anxiety.

They may provide short-term relief from anxiety symptoms, but long-term treatment strategies often involve alternative approaches, such as psychotherapy or other medications with a lower risk of dependence.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if benzodiazepines are a suitable option for managing your social anxiety. Benzodiazepines should never be used without the careful guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional.
For a comprehensive exploration of benzodiazepines for social anxiety, we invite you to read our in-depth article by clicking here. It covers the benefits and risks associated with their use in the treatment of social anxiety.
Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are a class of medications primarily used to manage the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat, trembling, and sweating.
They work by blocking the effects of adrenaline, which is responsible for the body’s physiological response to anxiety-inducing situations.
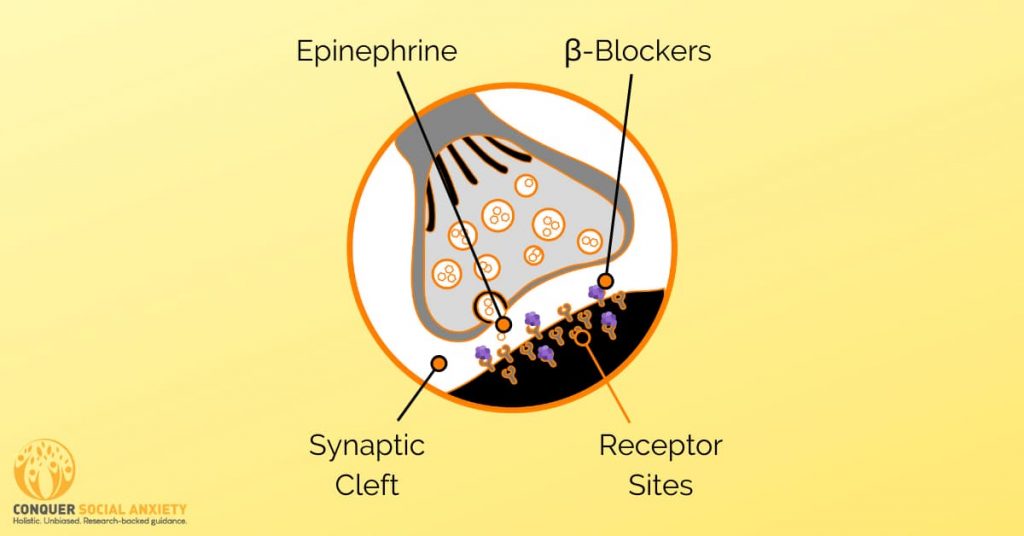
By reducing the physiological symptoms associated with anxiety, beta-blockers can help individuals cope with situations that trigger social anxiety.
One specific area where beta-blockers have been extensively studied is in the context of stage fright or performance anxiety.
Performance anxiety can be characterized by negative mood, increased heart rate, muscle tension, trembling, shortness of breath and other physical symptoms associated with anxiety.
In the field of social anxiety disorder, beta-blockers have been investigated as a strategy to reduce anxiety during exposure treatment.
For example, propranolol, a commonly prescribed beta-blocker, has been combined with exposure sessions to make anxiety more tolerable and enhance coping with feared situations.
Studies have shown that propranolol administration can lead to a decrease in anxiety (Morissette, Spiegel, & Barlow, 2007; Elsey et al., 2020). It has been found effective in fear neutralization during reconsolidation of fear memories related to public speaking (Soeter & Kindt, 2013).
By reducing the physiological symptoms associated with social anxiety, individuals may be able to function with fewer objective signs of anxiety (Elsey et al., 2020).
Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the suitability and safety of beta-blockers for managing social anxiety. A thorough evaluation and guidance from a healthcare professional are necessary to ensure the appropriate and effective use of beta-blockers in addressing individual needs and circumstances.
For a comprehensive understanding of beta-blockers for social anxiety, including their impact on physical symptoms, you can read our informative article by clicking here.
Other Medications
In some cases, healthcare professionals may consider other medications for social anxiety if the above options are not effective or appropriate for an individual.
For example, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors (RIMAs), can also be considered in certain situations, but require dietary restrictions and close monitoring due to potential interactions with certain foods and drugs (Thase, 2012).
It’s important to note that medication selection and usage depend on individual circumstances, including the severity of symptoms, medical history, and potential interactions with other medications. The choice of medication and treatment plan should always be determined by a qualified healthcare professional.
For a comprehensive understanding of MAOIs for social anxiety, you can click here to read our in-depth article discussing their benefits, evidence of their effectiveness, as well as their considerable risks and side effects.
For a comprehensive understanding of RIMAs for social anxiety, you can click here to read our in-depth article discussing their benefits, effectiveness, as well as their risks and potential side effects.
Exploring CBD as an Alternative to Medication
In recent years, there has been growing interest in CBD (cannabidiol) as a potential alternative to traditional medication for social anxiety.
CBD is a non-intoxicating compound derived from the cannabis plant, and it has shown promise in reducing anxiety symptoms.

However, it’s important to note that while research around the world is accumulating with promising results, more studies are needed to fully understand the effects and optimal use of CBD for social anxiety.
CBD interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in regulating mood, stress response, and emotional well-being.
Some research suggests that CBD may have anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) properties, potentially helping to reduce social anxiety symptoms (e.g. Bergamaschi et al., 2011, Fliegel & Lichtenstein, 2022; Masataka, 2019).
When considering CBD as an alternative, it’s crucial to choose products that are specifically labeled as CBD and contain little to no THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the psychoactive compound in cannabis. CBD products without THC are widely available and legal in many regions.

It’s important to note that individual experiences with CBD may vary, and it may not be effective for everyone. Some individuals find that CBD helps reduce their social anxiety symptoms, while others may not experience the same benefits.
As research on CBD continues to evolve, it’s important to stay informed and consult with a healthcare professional to make informed decisions about integrating CBD or any alternative treatments into your social anxiety management plan.
For our in-depth guide on using CBD to effectively manage symptoms of social anxiety, including scientific evidence, mechanisms of action, and a specific product recommendation for individuals with social anxiety, we invite you to click here.

D. Possible Side Effects and Risks Associated with Medication Use
While medications can be beneficial in treating social anxiety, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects and risks. Here are some considerations to keep in mind:
Side Effects
Medications used for social anxiety can cause side effects, although their frequency and severity vary among individuals. Common side effects may include:
- SSRIs and SNRIs: Nausea, headache, drowsiness, sexual dysfunction, gastrointestinal issues, and potential weight changes.
- Benzodiazepines: Drowsiness, dizziness, impaired coordination, memory issues, and potential dependency.
- Beta-Blockers: Fatigue, dizziness, low blood pressure, and potential heart rate irregularities.
- Other medications: Side effects vary depending on the specific medication. Consult with your healthcare provider to understand the potential side effects associated with any prescribed medication.

It’s important to remember that not everyone will experience these side effects, and they may diminish over time as your body adjusts to the medication.
If you experience any concerning or persistent side effects, inform your healthcare provider to explore possible solutions or alternative treatments.
Individual Variations
Again, each person’s response to medication can vary. What works well for one individual may not be as effective for another.
It may take some trial and error to find the most suitable medication and dosage for your specific needs.
Close communication with your healthcare provider is essential to monitor your response and make any necessary adjustments to optimize your treatment plan.

Potential Risks
Some medications used for social anxiety carry potential risks, including:
- Benzodiazepines: Long-term use or misuse of benzodiazepines can lead to dependency and withdrawal symptoms. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance and use these medications as prescribed.
- Antidepressant-related risks: In rare cases, certain antidepressants, including SSRIs and SNRIs, may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts, especially in younger individuals. It’s crucial to closely monitor changes in mood or behavior and seek immediate medical attention if you or someone you know experiences such changes.
It’s important to weigh the potential risks against the potential benefits of medication use. Your healthcare provider will consider your individual circumstances and medical history to determine the most appropriate treatment options while minimizing potential risks.
Treatment Monitoring
Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor the effectiveness of the medication and manage any side effects or risks.
Be sure to attend these appointments and communicate any concerns or changes in your symptoms.

E. Exploring the Combination of Medication with Therapy
Typically, medication is not recommended as a standalone treatment for social anxiety disorder. In most cases, it is prescribed in combination with psychotherapy or other therapeutic approaches to enhance overall effectiveness.
This combined approach of both medication and psychotherapy is often considered the standard approach for managing social anxiety.
Medication can help alleviate symptoms and provide immediate relief, while therapy addresses the underlying causes and helps individuals develop long-term coping skills.
This combination approach allows individuals to experience symptom reduction, learn effective strategies, and gain a deeper understanding of their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.

Psychotherapies
There is a wide range of psychotherapies that have been shown to effectively reduce social anxiety.
The most common and well-researched therapy for social anxiety is Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which includes techniques such as cognitive restructuring, exposure therapy, and social skills training.

CBT helps individuals identify and modify negative thought patterns, challenge irrational beliefs, and develop effective coping strategies. You can click here to be taken to our introductory guide to CBT for social anxiety.
Another valid alternative is psychodynamic therapy, which explores the underlying causes of social anxiety and focuses on gaining insight into unconscious patterns and early experiences.
To delve deeper into the topic of psychodynamic therapy for social anxiety, we invite you to click here and explore our comprehensive introductory resource.
Exploring Alternative Therapies
In addition to CBT and psychodynamic therapy, there are other alternative therapies that individuals may consider for social anxiety. These may include acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and mindfulness-based therapies.
These approaches offer different perspectives and techniques to address social anxiety. For more information on alternative therapies, we recommend referring to our ebook. Click here to learn more about the ebook and access additional resources.

It’s important to discuss the combination of medication with therapy or other treatments with your healthcare provider.
They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific needs and circumstances.
Collaboration between your healthcare provider and therapist is also beneficial to ensure coordination and an integrated treatment plan.
Recommended: Comprehensive Online Therapy and Psychiatric Service
If you’re seeking a thorough and effective way to address social anxiety, combining medication with therapy is the most promising option for most individuals. In this regard, we wholeheartedly endorse Brightside as an excellent option.
Brightside‘s team of licensed therapists specializes in the treatment of anxiety, offering strategies that are backed by solid evidence.
By integrating therapy with expert-guided medication management, Brightside provides a holistic solution for effectively managing and conquering social anxiety.

This combined approach is particularly recommended for individuals who are grappling with overwhelming symptoms and are eager for prompt relief.
What sets this approach apart is its focus on not just short-term relief, but also on understanding and addressing the root causes of social anxiety.
This empowers individuals to not only find relief in the present but also work towards lasting independence from medication.
Choosing Brightside means selecting a path that offers a comprehensive and personalized strategy, led by professionals who are committed to helping you regain control over your social anxiety and lead a more fulfilling life.

F. Guidance & Advice for Working with a Healthcare Provider
Recognize the importance of professional help
Once again, if you’re experiencing symptoms of social anxiety, it’s crucial to seek professional guidance.
A healthcare provider, such as a psychiatrist, psychologist, or primary care physician, can assess your condition, provide an accurate diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
They have the expertise to guide you through the process and help you find the most effective strategies to manage social anxiety.

Find a qualified healthcare provider
Look for a healthcare provider who specializes in anxiety disorders or has experience in treating social anxiety.
Seek recommendations from trusted sources, such as your primary care physician, friends, or family members who have had positive experiences with mental health professionals.
You can also consult online directories or professional organizations to find qualified providers in your area.

Recommended Online Psychiatry Service
You can conveniently schedule an online appointment with a qualified psychiatrist, licensed in your state, through our following partner-link, which also offers a special discount code.
The psychiatrists from Talkspace can provide a comprehensive evaluation, offer a diagnosis if applicable, and prescribe medication, such as those discussed above, if deemed appropriate for your specific needs.
Your prescription will be sent to a local pharmacy of your choice. Every three months you’ll have a follow-up video appointment, and you can message your provider any time.
Prescription treatment with Talkspace costs you about $30/month if you are insured, and about $60-$100/month when you pay out-of-pocket. Remember, through our link you will get a special coupon code.
Be open and honest during the assessment
When you consult with a healthcare provider, be open and honest about your symptoms, concerns, and goals.
This information will help them better understand your unique situation and tailor the treatment approach to your specific needs.
Don’t hesitate to ask questions or seek clarification if you’re unsure about any aspect of your diagnosis or treatment plan.

Collaborate on treatment decisions
Treatment for social anxiety should be a collaborative process between you and your healthcare provider. Discuss the available treatment options, including medication, therapy, or a combination of both.
Consider the potential benefits, risks, and side effects of each option. Together, you can make informed decisions that align with your preferences and treatment goals.
Follow the recommended treatment plan
Once a treatment plan is established, it’s important to follow it consistently.
If medication is prescribed, take it as prescribed and inform your healthcare provider of any concerns or side effects you experience.
If therapy is recommended, attend sessions regularly and actively participate in the therapeutic process.
Communicate openly with your healthcare provider about your progress, challenges, and any adjustments that may be needed.

Practice patience and give it time
Treating social anxiety often requires time and patience. Medication effects may take several weeks to become noticeable, and therapy is a process that unfolds gradually.
Be realistic about your expectations and understand that progress may come in small steps. Consistency and commitment to the treatment plan will increase the likelihood of positive outcomes.
Communicate openly
Throughout your treatment journey, maintain open communication with your healthcare provider.
Share your progress, concerns, and any changes in your symptoms. This will allow them to make appropriate adjustments to your treatment plan, ensuring it remains effective and tailored to your evolving needs.
Remember, seeking professional guidance is an important step towards managing social anxiety effectively.
With the support and expertise of a healthcare provider, you can develop strategies and access resources that will help you navigate social situations with greater confidence and ease.

G. Conclusion
Medication can be a valuable treatment option for social anxiety, helping individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
While it’s important to recognize the benefits of medication, it’s equally important to consider the limitations, potential side effects, and individual variations in response.
Remember, social anxiety is a complex condition, and what works for one person may not work for another.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis, discuss the available treatment options, and guide you toward an individualized treatment plan.
A healthcare professional can help you navigate the various medications used for social anxiety, considering factors such as your specific symptoms, medical history, and personal preferences.

They can also assess the potential benefits and risks associated with each medication, monitor your progress, and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
In addition to medication, therapy, such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and other alternative treatments can play a crucial role in managing social anxiety.
The combination of medication and therapy, tailored to your unique needs, can provide a comprehensive approach to addressing both the physiological and psychological aspects of social anxiety.
We strongly encourage you to reach out to a healthcare professional who specializes in anxiety disorders or mental health. They can provide the guidance, support, and expertise needed to develop an effective treatment plan for your social anxiety.
Remember, you don’t have to face social anxiety alone. Seeking professional help is a brave and important step toward overcoming the challenges of social anxiety and living a fulfilling life.
For a comprehensive guide on the treatment of social anxiety, we invite you to explore our complete treatment guide by clicking here. It provides in-depth information and valuable insights to help you better understand and manage social anxiety.
Participate in a Research Study!
If you are affected by social anxiety, you can help researchers and clinicians better understand the condition and improve treatment efficacy by participating in a research study.
To take part, you can click here to open a short, quick survey in a new browser window, or simply fill out the form provided below. Thank you for your participation!
Bergamaschi, M. M., Queiroz, R. H., Chagas, M. H., de Oliveira, D. C., De Martinis, B. S., Kapczinski, F., Quevedo, J., Roesler, R., Schröder, N., Nardi, A. E., Martín-Santos, R., Hallak, J. E., Zuardi, A. W., & Crippa, J. A. (2011). Cannabidiol reduces the anxiety induced by simulated public speaking in treatment-naïve social phobia patients. Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 36(6), 1219-1226. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2011.6
Elsey, J. W. B., Filmer, A. I., Galvin, H. R., Kurath, J. D., Vossoughi, L., Thomander, L. S., Zavodnik, M., & Kindt, M. (2020). Reconsolidation-based treatment for fear of public speaking: a systematic pilot study using propranolol. Translational psychiatry, 10(1), 179. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-0857-z
Fliegel, D. K., & Lichenstein, S. D. (2022). Systematic literature review of human studies assessing the efficacy of cannabidiol for social anxiety. Psychiatry research communications, 2(4), 100074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psycom.2022.100074
Licata, S. C., & Rowlett, J. K. (2008). Abuse and dependence liability of benzodiazepine-type drugs: GABA(A) receptor modulation and beyond. Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior, 90(1), 74–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2008.01.001
Masataka N. (2019). Anxiolytic Effects of Repeated Cannabidiol Treatment in Teenagers With Social Anxiety Disorders. Frontiers in psychology, 10, 2466. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02466
Mitsui, N., Fujii, Y., Asakura, S., Imai, H., Yamada, H., Yoshinaga, N., Kanai, Y., Inoue, T., & Shimizu, E. (2022). Antidepressants for social anxiety disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology reports, 42(4), 398–409. https://doi.org/10.1002/npr2.12275
Morissette, S. B., Spiegel, D. A., & Barlow, D. H. (2008). Combining exposure and pharmacotherapy in the treatment of social anxiety disorder: A preliminary study of state dependent learning. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 30(3), 211–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-007-9061-1
Soeter, M., & Kindt, M. (2013). High trait anxiety: a challenge for disrupting fear memory reconsolidation. PloS one, 8(11), e75239. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075239
Thase M. E. (2012). MAOIs and depression treatment guidelines. The Journal of clinical psychiatry, 73(7), e24. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.11096tx4c
Williams, T., Hattingh, C. J., Kariuki, C. M., Tromp, S. A., van Balkom, A. J., Ipser, J. C., & Stein, D. J. (2017). Pharmacotherapy for social anxiety disorder (SAnD). The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 10(10), CD001206. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001206.pub3

About the Author: Martin Stork
Martin is a professional psychologist with a background in physical therapy. He has organized and led various support groups for people with social anxiety in Washington, DC and Buenos Aires, Argentina. He is the founder of Conquer Social Anxiety Ltd, where he operates as a writer, therapist and director. You can click here to find out more about Martin.






